Cells and cell organelles worksheet answers – Delve into the fascinating world of cells and their organelles with our comprehensive worksheet answers. Discover the intricate workings of these microscopic marvels, from the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells to the specialized functions of each organelle. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of cell division, transport, communication, metabolism, and more, as we embark on an academic journey that will illuminate the very foundation of life.
1. Types of Cells: Cells And Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
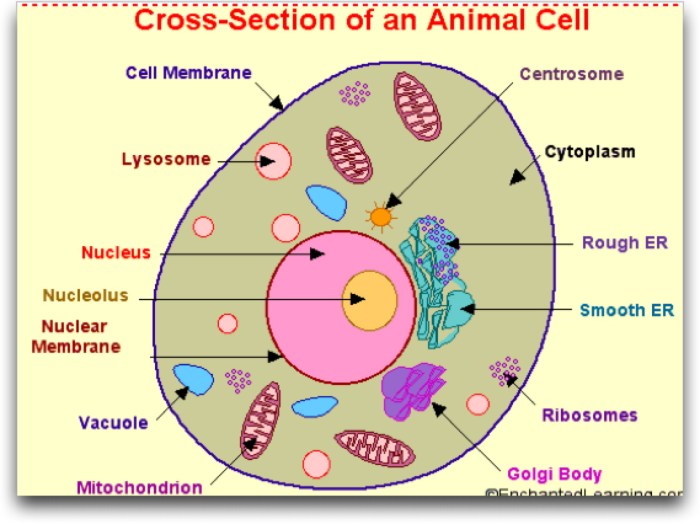
Cells are the fundamental units of life, and they come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The two main types of cells are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and contain a nucleus and other organelles.
Prokaryotic Cells, Cells and cell organelles worksheet answers
- Lack a nucleus
- Lack membrane-bound organelles
- Typically smaller than eukaryotic cells
- Found in bacteria and archaea
Eukaryotic Cells
- Contain a nucleus
- Contain membrane-bound organelles
- Typically larger than prokaryotic cells
- Found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists
In addition to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, there are also animal cells and plant cells. Animal cells are typically round or oval in shape, while plant cells are typically rectangular in shape. Plant cells also have a cell wall, which is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane.
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells | Animal Cells | Plant Cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Membrane-bound organelles | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cell wall | No | No | No | Yes |
| Shape | Typically round or oval | Typically rectangular | Typically round or oval | Typically rectangular |
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess both.
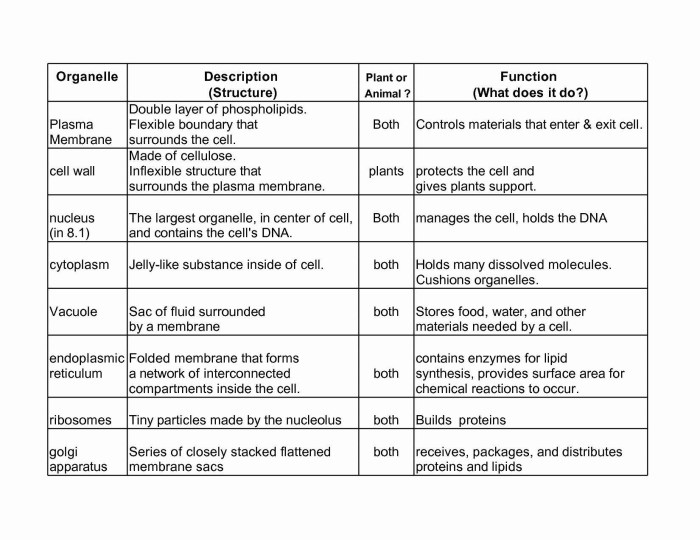
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or storage.
How does cell transport maintain cell homeostasis?
Cell transport mechanisms regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell, ensuring a stable internal environment.