As conscious and intentional recall crossword takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world of enhanced memory, where techniques and strategies are unveiled to optimize cognitive abilities. Drawing upon a foundation of neuroscience and cognitive psychology, we delve into the intricate mechanisms that govern our ability to consciously and intentionally access information, empowering individuals to harness the full potential of their minds.
This comprehensive exploration unravels the neural pathways and cognitive processes underlying conscious and intentional recall, shedding light on the interplay between attention, working memory, and metacognition. We examine the factors that influence retrieval effectiveness, such as context, retrieval cues, and individual differences, providing practical insights for optimizing memory performance.
Conscious and Intentional Recall
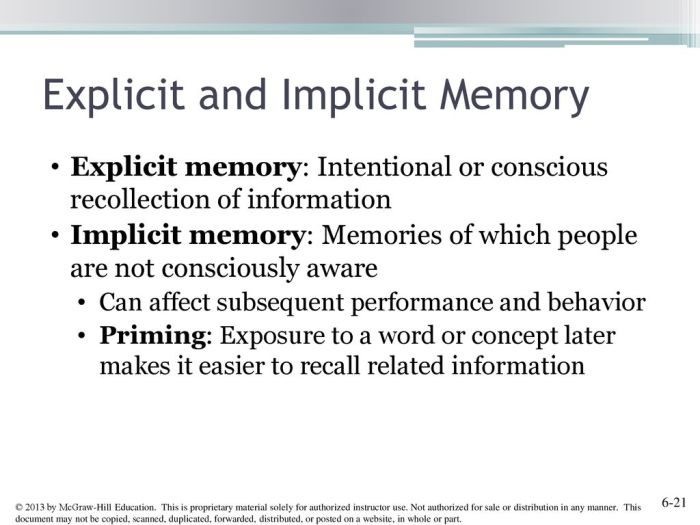
Conscious and intentional recall refers to the ability to retrieve information from memory in a deliberate and controlled manner. It is a type of memory retrieval that is distinct from automatic recall, which occurs spontaneously without conscious effort.
Neural Mechanisms of Conscious and Intentional Recall
Conscious and intentional recall involves a complex network of brain regions and neural pathways. Key structures involved include:
- Hippocampus: Involved in memory formation and consolidation
- Prefrontal cortex: Responsible for executive functions, including attention and working memory
- Amygdala: Involved in emotional processing and memory
Cognitive Processes Involved in Conscious and Intentional Recall
Conscious and intentional recall involves several cognitive processes, including:
- Attention: Directing focus to relevant cues
- Working memory: Holding information in mind temporarily
- Metacognition: Monitoring and evaluating one’s own memory processes
Factors Influencing Conscious and Intentional Recall
The effectiveness of conscious and intentional recall can be influenced by various factors, such as:
- Context: The environment in which information is learned and recalled
- Retrieval cues: Information that triggers memory retrieval
- Individual differences: Cognitive abilities, memory strategies, and motivation
Applications of Conscious and Intentional Recall: Conscious And Intentional Recall Crossword

Conscious and intentional recall has numerous applications in everyday life, including:
- Education: Studying for exams and recalling information
- Research: Conducting experiments and analyzing data
- Clinical settings: Assessing memory function and diagnosing disorders
Future Directions in Research on Conscious and Intentional Recall
Despite significant progress, our understanding of conscious and intentional recall is still incomplete. Future research directions include:
- Investigating the role of sleep and consolidation
- Exploring the neural mechanisms underlying metacognition
- Developing interventions to improve memory retrieval
Query Resolution
What is the difference between conscious and intentional recall?
Conscious recall involves actively retrieving information from memory, while intentional recall specifically refers to retrieving information that has been consciously targeted for retrieval.
What are the key brain regions involved in conscious and intentional recall?
The hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and other brain structures play crucial roles in conscious and intentional recall, supporting memory encoding, consolidation, and retrieval.
How can I improve my conscious and intentional recall abilities?
Engaging in active retrieval practices, such as recalling information without cues or using spaced repetition, can enhance conscious and intentional recall.