Fenestrated vs non fenestrated drape – In the realm of healthcare and surgical procedures, the distinction between fenestrated and non-fenestrated drapes holds significant importance. This article delves into the intricacies of these specialized drapes, exploring their unique characteristics, applications, and regulatory considerations.
Fenestrated drapes, featuring strategically placed openings or windows, offer distinct advantages in surgical settings, while non-fenestrated drapes provide a more comprehensive barrier against contamination. Understanding the nuances between these two types of drapes is crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimal outcomes.
Definition and Overview
Fenestrated and non-fenestrated drapes are two types of window treatments that differ in their design and functionality.
Fenestrated drapesare window coverings that feature cutouts or openings that allow light and air to pass through. These cutouts can be of various shapes and sizes, such as circles, ovals, or geometric patterns. Fenestrated drapes provide privacy while still allowing natural light to filter into the room.
Non-fenestrated drapes, on the other hand, are solid window coverings that do not have any cutouts or openings. They provide complete privacy and light blockage, making them suitable for bedrooms or media rooms where darkness is desired.
Comparison of Key Features
The following table compares the key features of fenestrated and non-fenestrated drapes:
| Feature | Fenestrated Drapes | Non-Fenestrated Drapes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Fabric, sheer, or lace | Fabric, velvet, or blackout material |
| Construction | Cutouts or openings | Solid, no openings |
| Applications | Privacy while allowing light | Complete privacy and light blockage |
Applications and Benefits
Fenestrated drapes are specialized medical drapes with strategically placed openings that allow access to specific surgical sites while maintaining a sterile field. They are primarily used in surgical procedures to facilitate access to anatomical structures without compromising sterility.
Advantages of Fenestrated Drapes
- Precise access to surgical sites, reducing the risk of surgical site infections.
- Improved visibility and visualization of the surgical area, leading to greater surgical precision.
- Reduced risk of surgical instrument contamination, as only the necessary areas are exposed.
- Enhanced patient comfort by minimizing the need for repositioning during surgery.
Disadvantages of Fenestrated Drapes
- Increased risk of surgical site contamination if not properly positioned or sealed.
- Higher cost compared to non-fenestrated drapes.
- Potential for increased surgical time if the fenestrations are not correctly aligned.
Examples of Fenestrated Drape Applications
- Orthopedic surgery:Accessing specific anatomical landmarks for joint replacement or fracture repair.
- Neurosurgery:Providing targeted access to cranial and spinal structures.
- Cardiac surgery:Facilitating precise access to the heart and major blood vessels.
- Gynecological surgery:Enabling access to reproductive organs during laparoscopic procedures.
Design and Construction
Fenestrated drapes are designed with a series of evenly spaced openings or “fenestrations” that allow for controlled light transmission and ventilation. These fenestrations are typically circular or elliptical in shape and are strategically placed to optimize airflow and natural lighting.
The construction of fenestrated drapes involves several steps. First, the base fabric is selected. This fabric can be made from a variety of materials, including polyester, nylon, or cotton. The fabric is then cut into the desired shape and size, and the fenestrations are created using a laser cutter or other precision cutting tool.
Materials Used
The materials used in the construction of fenestrated drapes play a significant role in their performance and functionality. Polyester is a popular choice due to its durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture resistance. Nylon is another commonly used material, offering high strength and abrasion resistance.
Cotton is a natural fiber that provides a soft and comfortable feel, but it is less durable and more prone to wrinkling than synthetic materials.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of fenestrated drapes involves several steps, including fabric preparation, cutting, fenestration creation, and finishing. Fabric preparation involves treating the fabric to ensure proper adhesion of coatings or treatments. Cutting involves using precision tools to cut the fabric into the desired shape and size.
Fenestration creation is achieved using laser cutting or other precision cutting techniques. Finally, finishing involves applying any necessary coatings or treatments to enhance the drape’s performance and durability.
Design Features
The design features of fenestrated drapes significantly impact their performance and functionality. The size, shape, and spacing of the fenestrations determine the amount of light transmission and airflow. The location of the fenestrations also plays a role, with fenestrations placed near the top of the drape providing more natural lighting and those placed near the bottom providing more ventilation.
In addition to the fenestrations, other design features of fenestrated drapes include the use of grommets or other hanging systems, as well as the addition of decorative elements such as trims or borders.
Sterilization and Maintenance
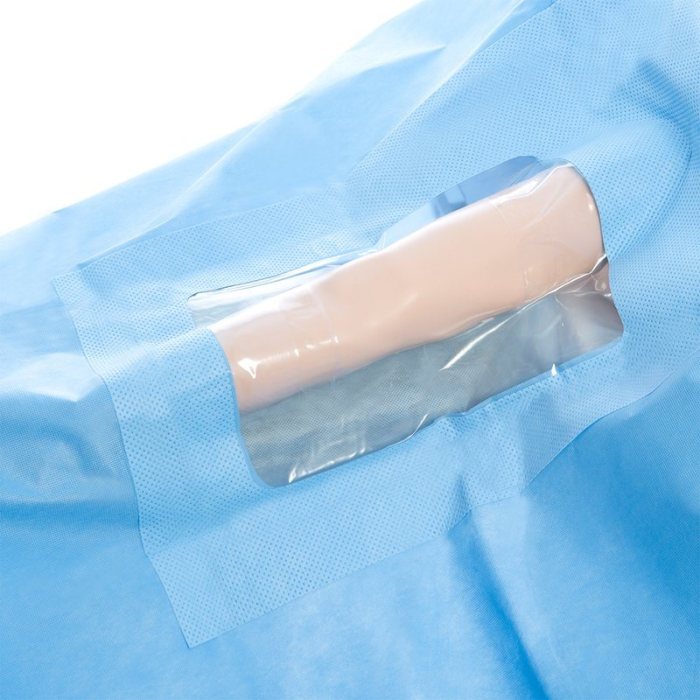
Proper sterilization and maintenance of fenestrated drapes are crucial to prevent contamination and ensure patient safety. These drapes undergo a rigorous process to ensure their sterility before surgical use.
The sterilization process typically involves:
- Pre-cleaning to remove visible soil and debris.
- Machine washing using approved detergents and disinfectants.
- Rinsing and drying to remove chemical residues.
- Packaging in sterile containers or pouches.
Once sterilized, fenestrated drapes must be handled and stored properly to maintain their sterility.
Guidelines for Care and Maintenance
Guidelines for the care and maintenance of fenestrated drapes include:
- Inspecting drapes for any tears or damage before each use.
- Following manufacturer’s instructions for laundering and sterilization.
- Storing drapes in a clean, dry environment.
- Discarding drapes if they become contaminated or damaged.
By adhering to these guidelines, healthcare facilities can ensure the proper sterilization and maintenance of fenestrated drapes, reducing the risk of infection and protecting patient safety.
Regulatory Considerations
Fenestrated drapes are medical devices subject to regulatory standards and guidelines to ensure patient safety and product quality.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies fenestrated drapes as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification and compliance with specific design and performance criteria.
Certification and Accreditation
Fenestrated drapes can undergo voluntary certification or accreditation processes to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- ISO 13485:2016: International standard for quality management systems for medical devices.
- AAMI ANSI/AAMI/ISO 11137-1:2018: Standard for surgical drapes, gowns, and clean air suits used in operating rooms and other controlled environments.
Compliance with these standards ensures that fenestrated drapes meet specified performance requirements, such as fluid resistance, microbial barrier, and drape integrity.
Market Trends and Future Developments
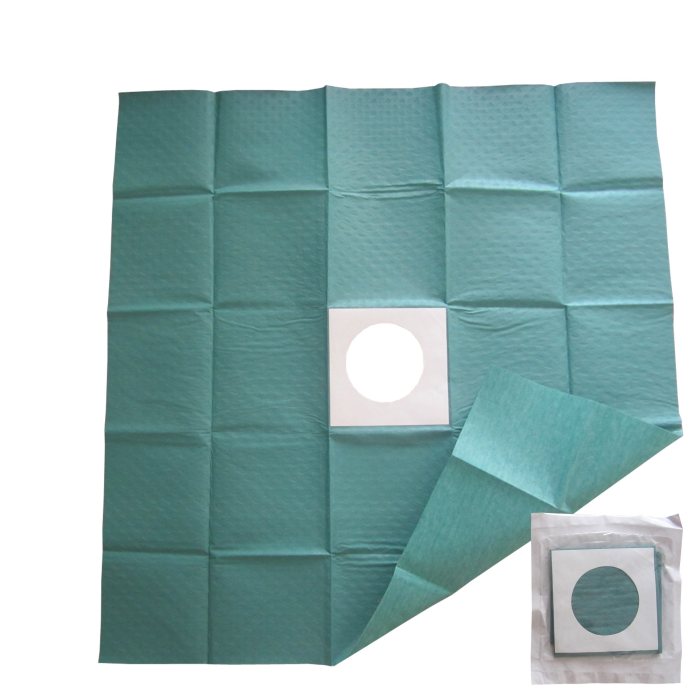

The fenestrated drape market is witnessing a surge in demand, driven by advancements in surgical techniques and increasing adoption of minimally invasive procedures. Technological innovations and research are shaping the future of fenestrated drapes, leading to improved functionality, patient outcomes, and cost-effectiveness.
Technological Advancements
- Enhanced Imaging Capabilities:Fenestrated drapes with integrated imaging windows allow surgeons to visualize the surgical site without compromising the sterile field. This improves accuracy and reduces the risk of complications.
- Antimicrobial Properties:Antibacterial and antiviral coatings are being incorporated into fenestrated drapes to prevent the spread of infections and enhance patient safety.
- Biodegradable Materials:The use of biodegradable materials in fenestrated drapes promotes sustainability and reduces environmental impact.
Future Growth and Opportunities, Fenestrated vs non fenestrated drape
The growing demand for minimally invasive surgeries, coupled with technological advancements, is expected to drive the growth of the fenestrated drape market in the coming years. Opportunities for innovation include:
- Customizable Fenestrations:Developing drapes with customizable fenestration patterns to meet the specific needs of different surgical procedures.
- Integrated Surgical Devices:Incorporating surgical instruments or devices into fenestrated drapes to enhance functionality and efficiency.
- Telemedicine Integration:Integrating fenestrated drapes with telemedicine platforms to enable remote surgical assistance and training.
Essential FAQs: Fenestrated Vs Non Fenestrated Drape
What are the key differences between fenestrated and non-fenestrated drapes?
Fenestrated drapes have strategically placed openings or windows, while non-fenestrated drapes are continuous barriers without any openings.
What are the advantages of using fenestrated drapes?
Fenestrated drapes allow for visualization and access to specific areas of the surgical site, facilitating precise surgical procedures.
What are the disadvantages of using non-fenestrated drapes?
Non-fenestrated drapes provide a more comprehensive barrier against contamination but may limit access to certain areas of the surgical site.
What regulatory standards apply to fenestrated drapes?
Fenestrated drapes are subject to regulatory standards established by organizations such as the FDA and other healthcare agencies to ensure patient safety and product quality.